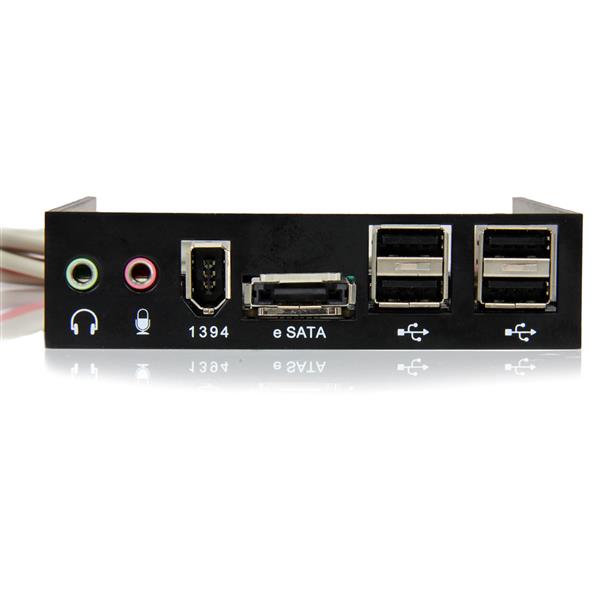


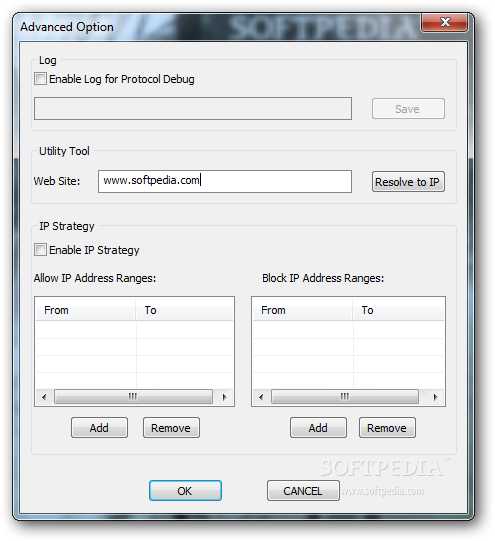
Using the command "ip a" will achieve the same results in a different format.Find the one you are using, and use the number after 'inet addr:'. It will list information for each of your network devices. If you don't have Network Manager, open a Terminal and type 'ifconfig'.On Unix- In Ubuntu, right-click the Network Manager applet in the menu bar, and select 'Connection Information'.On macOS- Go to System Preferences > Network, double-clicking on your connection (for instance, Built-in Ethernet), and clicking the TCP/IP tab.If Transmission reports that the 'Port is open' then you have successfully port forwarded!.Go to Preferences > Network > Ports, and check 'Forward port from router'.Most routers manufactured since 2001 have either the UPnP or NAT-PMP feature. NAT-PMP / UPnPīy default Transmission will try to forward this port for you, using UPnP or NAT-PMP. To allow other peers to connect to you, you will need to forward a port from the router to your computer.
#PORT FORWARDING WIZARD WINDOWS#
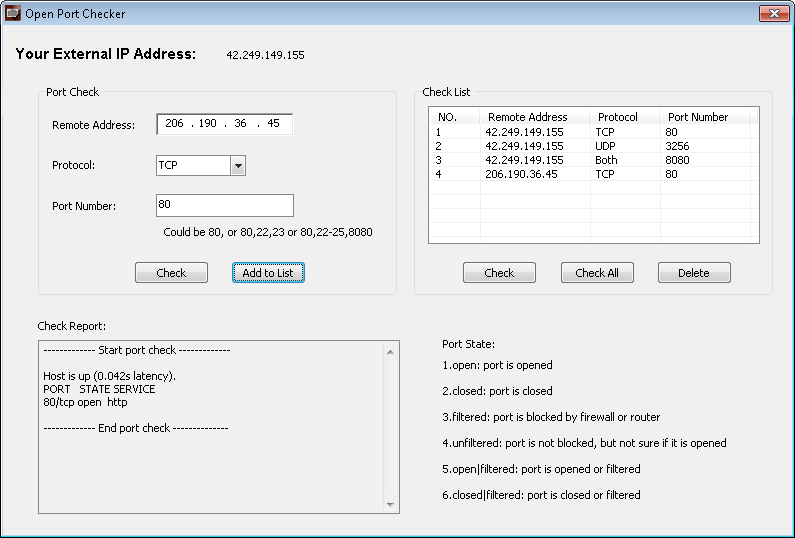
Choose the profile according to the type of network you are connected to and hit "Next".Here in "Actions" you choose to either "Allow the connection", "Allow the connection if it is secure" (only allow packets using IPsec), choose based on personal preference here then click "Next".51413 is the default but you can set it to any port you like as long as it correlates with the port you have set in Transmission. Underneath that you choose what port to open. In "Protocols and Ports" select either TCP (for BT protocol) or UDP (for μTP) for which one you want to open (to open both you must now choose one and go back later and created another rule to select the other).With that being said, check the button next to "Port" and click "Next". Whilst there are a couple ways to go about things from here, here we will only cover opening just the port alone for TCP/UDP. This will bring up a new window titled "New Inbound Rule Wizard".Once you have the Inbound Rules list showing you want to click on "New Rule" under the "Actions" panel on the right.On the left panel click "Inbound Rules".This will prompt for administrator access. Choose "Advanced Settings" on the left panel.You need to ensure that Transmission's port (displayed in preferences) is forwarded in the firewall.
#PORT FORWARDING WIZARD HOW TO#
Make sure "Set access for specific services and applications" is selected. Open System Prefs > Security > Firewall.If this does not happen, you can add Transmission to Leopard's firewall manually: Upon opening Transmission for the first time, a macOS dialog box should appear asking if you will allow Transmission to receive incoming connections. To allow other peers to communicate with your Transmission instance, you have to forward a port through your firewall. Because of the nature of the Internet and security reasons, routers create a local network that makes your computer invisible to the Internet. However, this is not always as straightforward as it may seem. BitTorrent is a peer-to-peer protocol which allows users to send and receive bits of files without the need of it being hosted on a centralized server.įor this to be possible, it is required to be accessible from the Internet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
